As a bus slows down uniformly from 75.0 km/h, we embark on an exploration of uniform deceleration, delving into the intricate relationship between velocity, time, and distance traveled. This journey promises a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles governing this motion.
Uniform deceleration, a fundamental concept in physics, describes the constant decrease in velocity of an object over time. In this context, we will examine the deceleration of a bus, unraveling the factors that influence its gradual slowdown.
Uniform Motion Overview: A Bus Slows Down Uniformly From 75.0 Km/h

Uniform motion is a type of motion in which an object moves in a straight line with constant velocity. Velocity is a vector quantity that describes both the speed and direction of an object’s motion. In uniform motion, the object’s velocity does not change over time.
The relationship between velocity and time in uniform motion is given by the following equation:
v = d/t
where:
- v is the velocity of the object (m/s)
- d is the distance traveled by the object (m)
- t is the time taken by the object to travel the distance (s)
Uniform Deceleration, A bus slows down uniformly from 75.0 km/h
Uniform deceleration is a type of motion in which an object moves in a straight line with decreasing velocity. Acceleration is a vector quantity that describes the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. In uniform deceleration, the object’s acceleration is constant and opposite in direction to its velocity.
The relationship between acceleration, velocity, and time in uniform deceleration is given by the following equation:
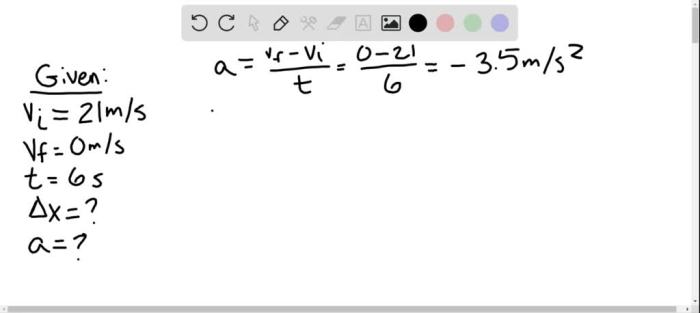
a = (v
u)/t
where:
- a is the acceleration of the object (m/s^2)
- v is the final velocity of the object (m/s)
- u is the initial velocity of the object (m/s)
- t is the time taken by the object to change its velocity (s)
Initial Conditions
The initial velocity of the bus is 75.0 km/h.
To convert the initial velocity from km/h to m/s, we use the following conversion factor:
1 km/h = 0.2778 m/s
Therefore, the initial velocity of the bus is:
u = 75.0 km/h
0.2778 m/s/km/h = 20.83 m/s
Final Velocity
The final velocity of the bus is 0 m/s.
This is because the bus is decelerating, which means its velocity is decreasing. The bus will continue to decelerate until its velocity reaches 0 m/s, at which point it will stop moving.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of the initial velocity in this scenario?
The initial velocity represents the speed at which the bus begins its deceleration. It is a crucial parameter in determining the distance traveled and the time taken to come to a complete stop.
How does the acceleration of the bus affect its deceleration?
Acceleration, in this context, refers to the rate of decrease in velocity. A higher acceleration will result in a more rapid deceleration, causing the bus to slow down more quickly.