Step into the realm of graphing distance vs time, where motion unravels in visual splendor. This comprehensive guide, “Graphing Distance vs Time Worksheet Answers,” embarks on a journey to demystify the intricate relationship between distance and time, equipping you with the tools to decipher the language of motion.
Prepare to navigate the intricacies of distance vs time graphs, unraveling their applications across diverse fields. Discover the art of constructing these graphs, interpreting their patterns, and extracting valuable insights into the dynamics of motion.
1. Graphing Distance vs Time Worksheet Answers
Distance vs time graphs are visual representations of the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time taken to travel that distance. They are commonly used in physics, engineering, and other fields to analyze motion and make predictions.
Creating a Distance vs Time Graph
- Gather data on the distance traveled and the corresponding time.
- Plot the data points on a graph with distance on the y-axis and time on the x-axis.
- Connect the data points with a line or curve.
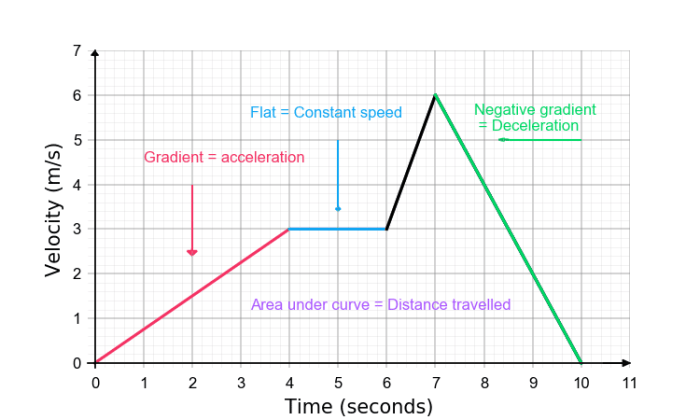
Interpreting Distance vs Time Graphs
- The slope of the line represents the speed of the object.
- The area under the curve represents the total distance traveled.
- The shape of the curve can indicate the type of motion (e.g., constant speed, acceleration, deceleration).
- An object travels 100 meters in 10 seconds. Calculate its speed.
- An object has an initial speed of 20 m/s and accelerates at 5 m/s². Calculate its speed after 10 seconds.
- Analyzing the motion of objects in projectile motion, free fall, and other scenarios.
- Determining the velocity and acceleration of objects.
- Designing and optimizing transportation systems.
- Analyzing the performance of machines and engines.
- Tracking the performance of athletes in running, cycling, and other sports.
- Developing training strategies to improve speed and endurance.
- Distance vs time graphs assume constant speed or acceleration, which may not always be the case.
- Advanced techniques, such as calculus, can be used to analyze more complex motion patterns.
2. Distance vs Time Calculations
Calculating Distance
The distance traveled can be calculated using the formula: distance = speed × time.
Calculating Speed
The speed can be calculated using the formula: speed = distance ÷ time.
Calculating Acceleration
The acceleration can be calculated using the formula: acceleration = (final speed – initial speed) ÷ time.
Practice Problems
3. Applications of Distance vs Time Graphs: Graphing Distance Vs Time Worksheet Answers
Physics
Engineering
Sports
4. Advanced Concepts
Non-Linear Motion, Graphing distance vs time worksheet answers
Distance vs time graphs can also represent non-linear motion, such as acceleration or deceleration with varying rates.
Graphing Multiple Objects
Distance vs time graphs can be used to compare the motion of multiple objects simultaneously.
Limitations and Extensions
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of the slope of a distance vs time graph?
The slope of a distance vs time graph represents the velocity of the object in motion.
How can distance vs time graphs be used to predict future motion?
By extrapolating the linear trend of a distance vs time graph, one can make predictions about the future position of the object.
What are the limitations of distance vs time graphs?
Distance vs time graphs assume constant velocity, which may not always be the case in real-world scenarios.