The body structure and directional terminology chapter 2 embarks on an illuminating journey into the intricacies of human anatomy, equipping readers with a profound understanding of the body’s architecture and the precise language used to navigate it. This chapter serves as a cornerstone for further exploration in healthcare, providing a solid foundation for comprehending medical diagnoses, treatment plans, and surgical procedures.
Through an in-depth examination of directional terminology, body planes, and regional divisions, this chapter unravels the complexities of human anatomy. It unveils the significance of surface anatomy and medical imaging techniques, empowering healthcare professionals with the tools to accurately assess and diagnose various medical conditions.
Body Structure and Directional Terminology
Understanding the body’s structure and directional terminology is crucial for healthcare professionals to accurately describe anatomical features, diagnose medical conditions, and perform medical procedures. This chapter provides a comprehensive overview of the terminology and concepts used to describe the human body.
Directional Terminology, The body structure and directional terminology chapter 2
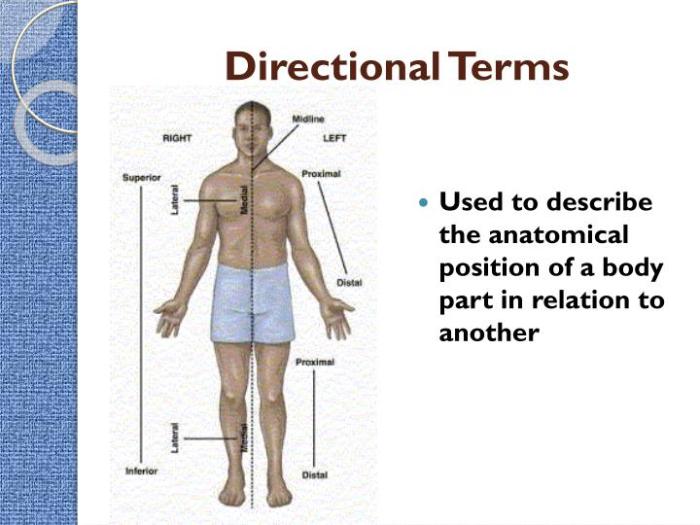
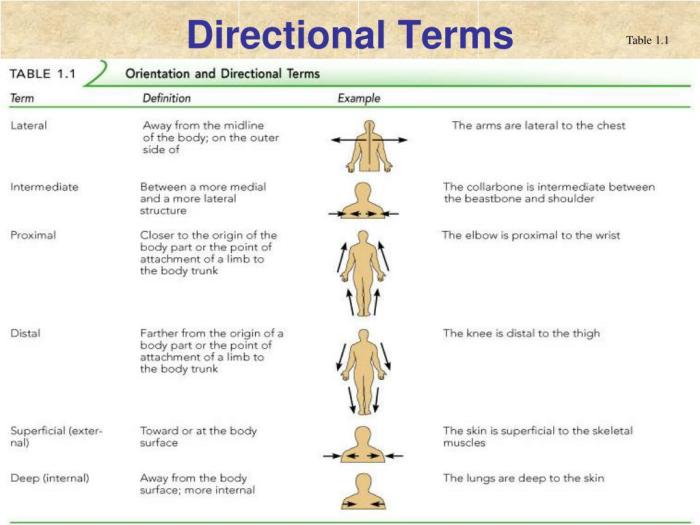
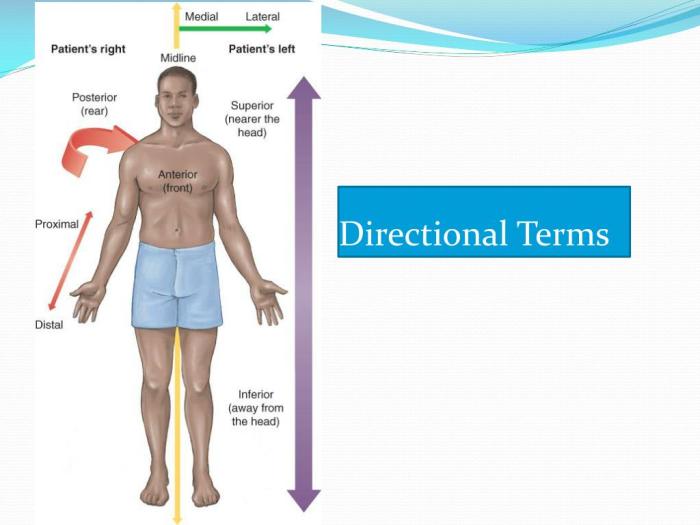
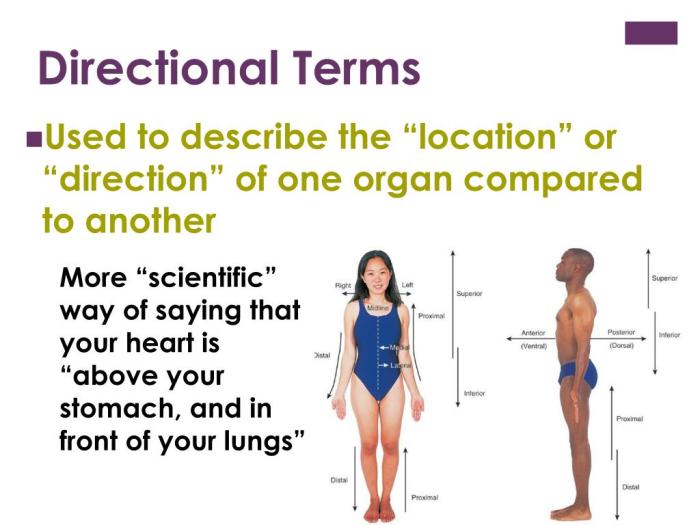
Directional terminology is used to describe the relative positions of body structures. The following terms are commonly used:
- Anterior: Front of the body
- Posterior: Back of the body
- Medial: Towards the midline of the body
- Lateral: Away from the midline of the body
- Proximal: Closer to the point of attachment
- Distal: Further from the point of attachment
- Superficial: Near the surface of the body
- Deep: Away from the surface of the body
Body Planes
The body can be divided into three primary planes:
- Sagittal plane: Divides the body into left and right halves
- Frontal plane: Divides the body into anterior and posterior halves
- Transverse plane: Divides the body into superior and inferior halves
Body Cavities
The body is divided into two main cavities:
- Dorsal cavity: Contains the brain and spinal cord
- Ventral cavity: Contains the heart, lungs, and digestive organs
Each cavity is further subdivided into smaller cavities, such as the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity.
Regional Terminology
The body is divided into several regions, including:
- Head: Contains the brain, eyes, ears, nose, and mouth
- Neck: Connects the head to the trunk
- Trunk: Contains the chest, abdomen, and pelvis
- Limbs: Include the arms and legs
- Extremities: Include the hands and feet
Surface Anatomy
Surface anatomy involves identifying and locating structures on the body’s surface. Landmarks, such as bones, muscles, and blood vessels, can be used to identify deeper structures.
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, allow healthcare professionals to visualize the body’s internal structures and diagnose medical conditions.
Clinical Applications
Understanding body structure and directional terminology is essential for healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and treat medical conditions. For example, it helps in:
- Performing physical examinations
- Interpreting medical images
- Planning and performing medical procedures
- Communicating with patients and other healthcare professionals
General Inquiries: The Body Structure And Directional Terminology Chapter 2
What is directional terminology?
Directional terminology is a system of terms used to describe the relative positions of body parts and structures.
What are the three primary body planes?
The three primary body planes are the sagittal plane, the frontal plane, and the transverse plane.
What are the two main body cavities?
The two main body cavities are the dorsal cavity and the ventral cavity.
What is surface anatomy?
Surface anatomy is the study of the external features of the body.
What are some medical imaging techniques?
Some medical imaging techniques include X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.